We encourage you to explore our Storm Streaming Server documentation. It covers
individual server configuration elements and provides information about popular
protocols such as RTMP, HLS, and more. The samples
directory also contains several example video players preconfigured to work with
your Storm Streaming Server instance.
For the next step we advise our Quick Start Guide
Linux/Unix Installation - Storm Streaming Server
Storm Streaming Server includes a user-friendly script-based installer for Unix/Linux systems,
which works in both GUI and console environments. Additionally, DEB and RPM package installers
are available from the download page.
If you don't have the installer yet, please visit our Download page.
Running the Installer
Before it is possible to run the installation script, it must be granted execution permissions. This can be done using the chmod command.
chmod +x storm_streaming_server_unix_aarch64_3_0_0.sh
Next we start the installer:
./storm_streaming_server_unix_aarch64_3_0_0.sh
Installer Steps (GUI Mode)
The installer will now guide you through the following steps:
-
Accept the Software License
In the first step, you must accept the software license agreement.
-
Enter the License Key
In the second step, you will be asked to enter the program license key. If you don’t have a license, you can leave this field blank. A developer license will be assigned instead, which allows up to 5 concurrent streams and a total of 10 viewers.
If you have a commercial or non-commercial license for Storm Streaming Server, you can view it on this page: https://www.stormstreaming.com/my-products
-
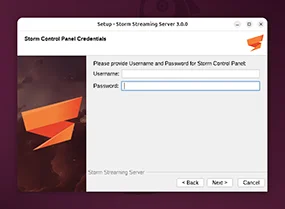
Provide Username and Password for Storm Control Panel
In this step, you need to provide the admin username and password for Storm’s web-based Control Panel.
-
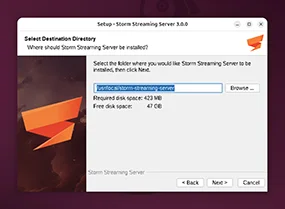
Choose Installation Location
In the fourth step, select the directory where the application will be installed.
-
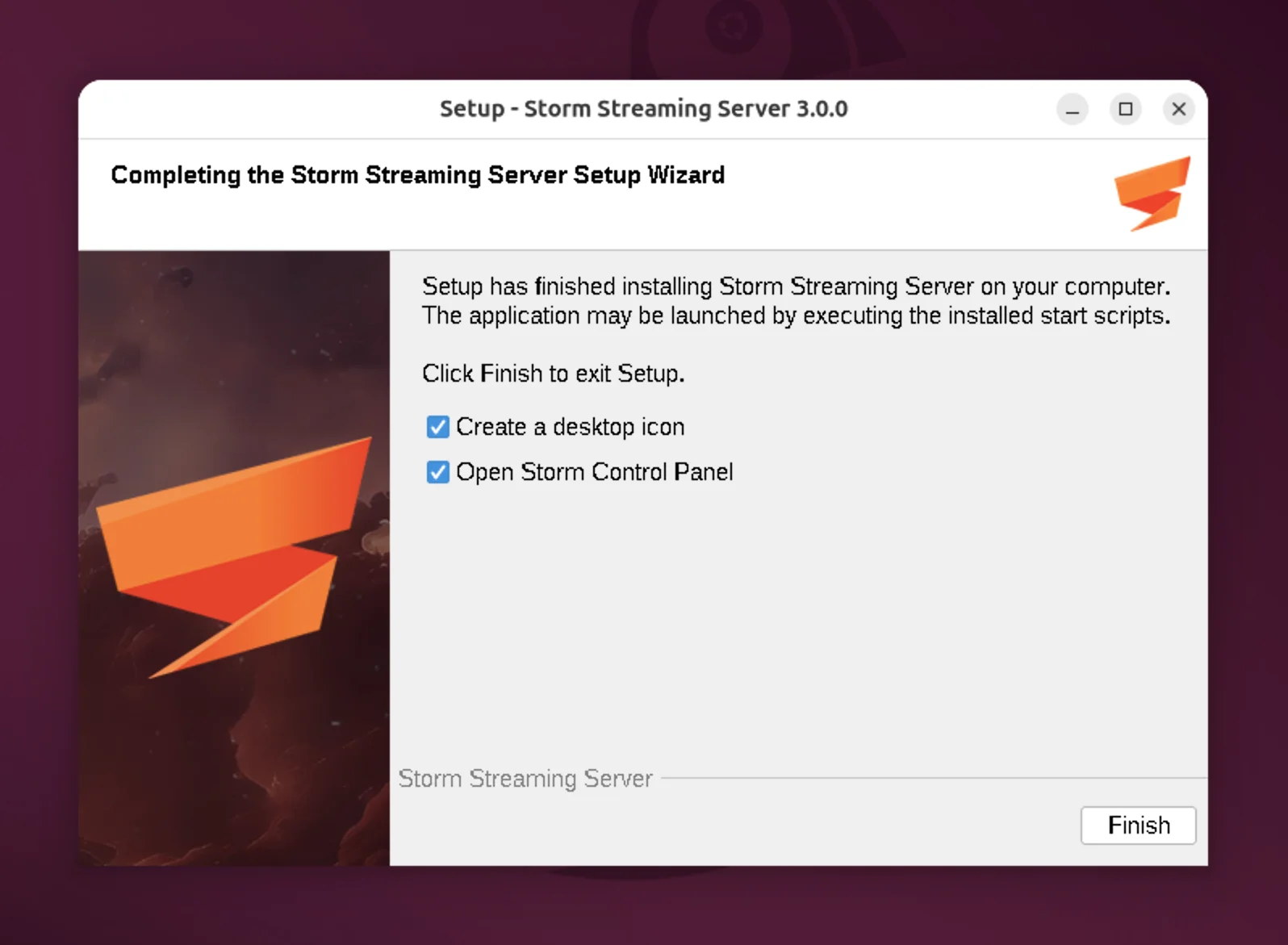
Optional Settings
In the final step, you can select a few additional options:- Create a desktop shortcut
- Open Storm Control Panel
Installer Steps (Console Mode)
If you manage your server via SSH or simply don't have a GUI, the console mode might come in handy. Just add -c as an additional parameter to the installer script.
./storm_streaming_server_unix_aarch64_3_0_0.sh -c
The rest is identical to the GUI counterpart.
Basic Configuration
Now that the Storm Streaming Server application is installed, go to the installation folder you specified in step 3. There are a few things to configure here:
-
JVM Configuration
In the file Storm storm-streaming-server.vmoptions, you'll find JVM options that define, among other things, how much RAM should be allocated to the application. The default file content is:
-server -Xmx16g -Xms4g -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=100The -Xms and -Xmx parameters define the minimum and maximum amount of RAM available to the application. You should adjust these values to match your hardware resources. For example, to allocate a maximum of 128 GB and a minimum of 32 GB, change the values to:
-Xmx128g -Xms32g -
VHost Configuration
The socket configuration for Storm Streaming Server is located in the file config/preferences.xml. By default, it includes the following block:
<VHosts> <VHost host="127.0.0.1" isSSL="false" port="1935"> <Protocols>RTMP</Protocols> </VHost> <VHost host="127.0.0.1" isSSL="false" port="8080"> <Protocols>HTTP, WEBSOCKETS</Protocols> </VHost> </VHosts>This defines two sockets listening on 127.0.0.1 (localhost). Port 8080 handles HTTP and WebSocksts connections, and port 1935 handles RTMP. For more information about VHost configuration, including how to enable SSL support, please refer to our VHosts guide.
Managing the Service
You can access the web-based control panel of the application using the 'Strom Control Panel' shortcut. Alternatively, you can open it directly in any web browser at: http://127.0.0.1/cpanel (the IP address and port may vary depending on your VHosts configuration).
Since the application operated as a service, it’ll be started automatically with the system. Below you’ll find basic commands:
-
To check the Storm Streaming Server (service) status:
systemctl status storm-streaming-server
-
To stop the Storm Streaming Server:
systemctl stop storm-streaming-server
-
To start the Storm Streaming Server:
systemctl start storm-streaming-server
-
To restart the Storm Streaming Server:
systemctl restart storm-streaming-server
At this point, a simple control panel is also available by default at (unless you modified VHOost): http://127.0.0.1:8080/cpanel
FFMPEG Installation (optional)
If the console shows a message about missing FFMPEG (required for stream transcoding), you can specify its path in the config/preferences.xml file. The configuration is found in the <Transcoder> block, like this:
<Transcoder>
<FFMPEG>
<Path>/opt/homebrew/bin/ffmpeg</Path> <!-- optional -->
<Command>-re -nostdin -i {SOURCE_INPUT} -vsync 1 -vcodec libx264 -preset:v {CPU_USAGE_PRESET} -vf scale={OUTPUT_WIDTH}:{OUTPUT_HEIGHT} -tune {TUNE} -g 30 -fflags nobuffer -probesize 32 -analyzeduration 0 -b:v {VIDEO_BITRATE} -acodec aac -b:a {AUDIO_BITRATE} -async 1 -f flv {STREAM_OUTPUT}</Command>
</FFMPEG>
<TranscodeTaskLimit>5</TranscodeTaskLimit>
<!-- remaining block -->
</Transcoder>
If FFMPEG has been added to the environment variables, you can leave the Path field empty — unless you want to explicitly specify which binaries should be used.
Depending on your operating system, you can use the following command to install FFMPEG via your
default package manager.
-
Debian / Ubuntu (apt)
sudo apt update sudo apt install ffmpeg
-
Arch Linux / Manjaro (pacman)
sudo pacman -Sy ffmpeg
-
macOS (Homebrew)
brew install ffmpeg
-
FreeBSD (pkg)
sudo pkg install ffmpeg
Create a free ticket and our support team will provide you necessary assistance.